Palestine Grid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Palestine grid was the
The Palestine grid was the  During
During
 The Palestine grid was the
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various ...
used by the Survey Department of Palestine.
The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini-Soldner projection. The central meridian
Meridian or a meridian line (from Latin ''meridies'' via Old French ''meridiane'', meaning “midday”) may refer to
Science
* Meridian (astronomy), imaginary circle in a plane perpendicular to the planes of the celestial equator and horizon
* ...
(the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery
Mar Elias Monastery ( he, מנזר אליהו הקדוש, ar, دير مار إلياس, Deir Mar Elias) is a Greek Orthodox monastery in south Jerusalem, on a hill overlooking Bethlehem and Herodium.
History
According to Christian tradition, E ...
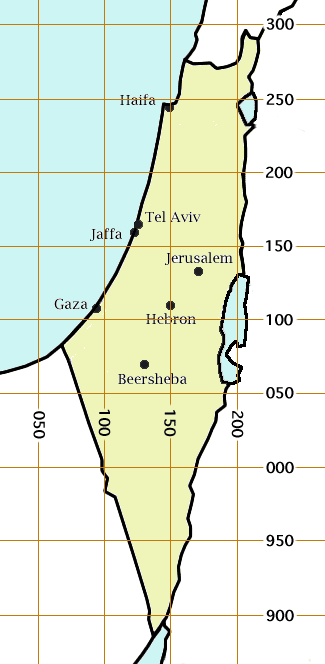
south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered.
At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative north-south coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by adding 1000 to the northern coordinate in that case. For some military purposes, 1000 was added to the north-south coordinates of all locations, so that they then ranged uniformly from about 900 to about 1300.
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, a Military Palestine Grid was used that was similar to the Palestine Grid but used the transverse Mercator
The transverse Mercator map projection (TM, TMP) is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection. The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the Universal Transverse Mercat ...
projection. The difference between the two projections was only a few metres.
After the establishment of the State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, the Palestine grid continued to be used under the name of the Israel Grid or the Israeli Cassini Soldner
Israeli Cassini Soldner (ICS), commonly known as the Old Israeli Grid (OIG; he, רשת ישראל הישנה ''Reshet Yisra'el Ha-Yeshana'') is the old geographic coordinate system for Israel. The name is derived from the Cassini Soldner projec ...
(ICS) grid, now called the "Old Israeli Grid", with 1000km added to the northing component to make the north-south range continuous. It was replaced by the Israeli Transverse Mercator
Israeli Transverse Mercator (ITM), also known as the New Israel Grid (NIG; he, רשת ישראל חדשה, רשת ישראל החדשה ''Reshet Yisra'el Ha-Ḥadasha'') is the new geographic coordinate system for Israel. The name is derived f ...
grid in 1994. The Palestine grid is still commonly used to specify locations in the historical and archaeological literature.
Specifying locations
The basic way of specifying a location on the Palestine grid is to write the east-west coordinate followed by the north-south coordinate using 3 digits each. For example, theDome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
is at 172132. This specifies the location within one kilometre. If more precision is required, extra digits can be added to each coordinate; for example, 17241317 gives the Dome of the Rock to within 100 metres. Many authors separate the two coordinates with punctuation for readability purposes, for example 172-132 or 172/132.For example, the location of Khirbet esh Sheik Mohammed is given as 1417.1984 in
References
{{reflistFurther reading
* Mugnier, Clifford J. (2000). ''Grids & Datums. The State of Israel'', Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 66, 2000, pp. 915-917, 933. Geographic coordinate systems Geography of Mandatory Palestine Land surveying systems Geodesy